| [1]Carnevale V, Romagnoli E, D'Erasmo L, et al. Bone damage in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2014; 24(11):1151-1157.
[2]Schwartz AV. Diabetes mellitus: dose it affect bone? Calcif Tissue Int. 2003;73(6):515-519.
[3]孙彦,李兴,朱亦堃,等.不同浓度葡萄糖对大鼠骨髓破骨细胞分化的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2007,13(4):239-242.
[4]Shao XY, Cao XJ, Song G, et al. Metformin rescues the MG63 osteoblasts against the effect of high glucose on proliferation. J Diabeted Res. 2014;2014:453940.
[5]Hofbauer LC, Brueck LC, Singh SK, SK et al. Osteoporosis in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22(9): 1317-1328.
[6]Bownlee M.The pathobiology of diabetic coplications:a unifying mechanism. J Diabetes. 2005;54(4):1615-1625.
[7]Chang YC, Chuang LM. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis oftype 2 diabetes: from molecular mechanism toclinical implication. Am J Transl Res. 2010;2(3):316-331.
[8]Hofbauer LC, Brueck CC, Singh SK, et al. Osteoporosis in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22(9):1317-1328.
[9]Danyelle M. Townsend, Kenneth D. Tew, Haim Tapiero,et al. The importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 2003;53(3-4):145-155.
[10]Pimson C, Chatuphonprasert W, Jarukamjorn K, et al. Improvement of antioxidant balance in diabetes mellitus type 1 mice by glutathione supplement. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014; 27(6):1731-1737.
[11]谢雅清,梁晓美,叶伟霞.还原型谷胱甘肽的药理作用与临床应用研究进展[J].中国药业,2013,22(7):124-127.
[12]张立婷,何琦熊,亚星,等.还原型谷胧甘肤对氧化应激所致肝脏损伤的作用机制[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2009,29(8):15-17.
[13]罗健华,那宇,张晓暄,等.还原型谷胱甘肽对糖尿病大鼠肾脏的保护作用及机制[J].吉林大学学报,2006,32(2):282-285.
[14]阿衣夏木古丽,陈锐.还原型谷胱甘肽防治化疗药物性肝损害效果观察[J].现代肿瘤医学,2011,19(2):352-354.
[15]罗蔚锋,包仕尧,刘春风.还原型谷肤甘肤治疗帕金森病的临床研究[J].中国临床神经科学,2003,11(2):195-197.
[16]汪瀚,鲍远程,张波,等.还原型谷胱甘肽治疗帕金森病38例临床观察.[J].中国实用医药,2006,1(1):13-15.
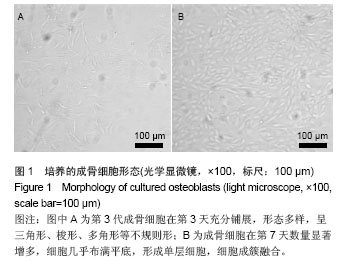
[17]王勇平,廖燚,蒋垚.成骨细胞的体外培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(33):6231-6234.
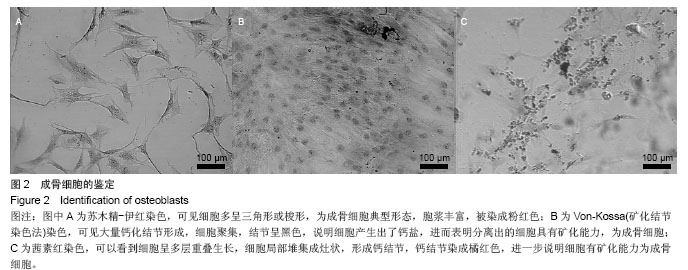
[18]廖乃顺,李钻芳,林如辉,等.比较3种形态学方法观察成骨细胞矿化结节的应用价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(33): 5266-5270.
[19]孙崇然,刘恩重.von Kossa 染色的方法改进[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2006,40(1):70-71.
[20]张静莹,齐民,杨大颐,等.ZnHA/TiO2复合涂层的制备及生物相容性[J].金属学报,2011,47(4):429-434.
[21]苏鑫,刘继乐,李新,等.胰岛素对糖尿病兔牙槽骨缺损修复的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(32):6240-6244.
[22]柳洪志,樊马娟,董立武,等.糖尿病兔与正常兔植入种植体骨整合对比研究[J].广东牙病防治,2009,17(9):415-418.
[23]拾莉,王健,韩光宇,等.糖尿病兔后肢缺血模型的制作[J].中国校医,2011,25(12):918-919.
[24]Volodymyr I. Lushchak. Glutathione homeostasis and functions: potential targets for medical interventions. J Amino Acids. 2012;2012:736837.
[25]Jackuliak P, Payer J. Osteoporosis, fractures, and diabetes. Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:820615.
[26]Giacco F, Brownlee M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ Res. 2010;107(9):1058-1070.
[27]Ceriello A. New insights on oxidative stress and diabetic complications may lead to a“causal” antioxidant therapy. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(5):1589-1596.
[28]袁平戈,张大志.还原型谷胱甘肽的作用机制及临床应用[J].药品评价,2006,3(5):385-390.
[29]Wu GY, Fang YZ, Yang S, et al. Glutathione metabolism and Its Implications for Health. J Nutr. 2004;134(3):489-492.
[30]李明,白晓春,刘俊,等.去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠血清中活性氧及抗氧化体系的变化[J].中国老年学杂志,2007,27(22):2164-2166. |
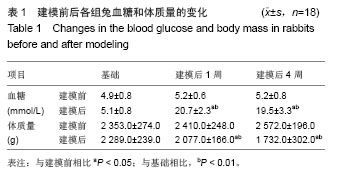
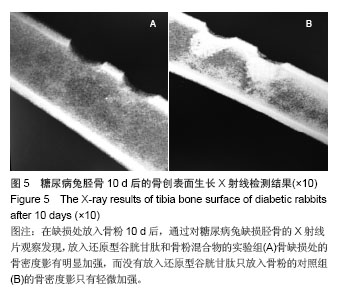
.jpg)